-
Lakewood:
(303) 922-4102 -
Westminster:
(303) 421-4140
What is a CVT? Understanding Continuously Variable Transmissions
Introduction to CVT
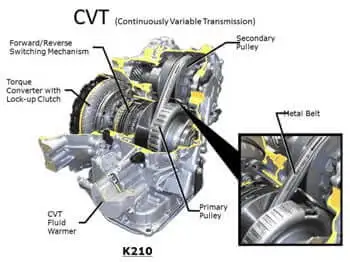
A Continuously Variable Transmission (CVT) is a type of automatic transmission that provides seamless acceleration without gear shifts. Unlike traditional transmissions that offer a limited number of gear ratios, CVT can adjust to any situation seamlessly, providing optimal engine performance and fuel efficiency. This versatility makes CVTs particularly valuable in modern vehicles where efficiency and performance are paramount.
CVTs stand out from traditional transmissions due to their unique ability to change seamlessly through an infinite number of effective gear ratios between maximum and minimum values. This distinction is not just technical but practical, offering drivers a smoother riding experience without the typical shift shocks found in conventional systems.
Learn more about the uniqueness of CVTs on our detailed page: What is Different About a CVT Transmission?
How Does A CVT Work?
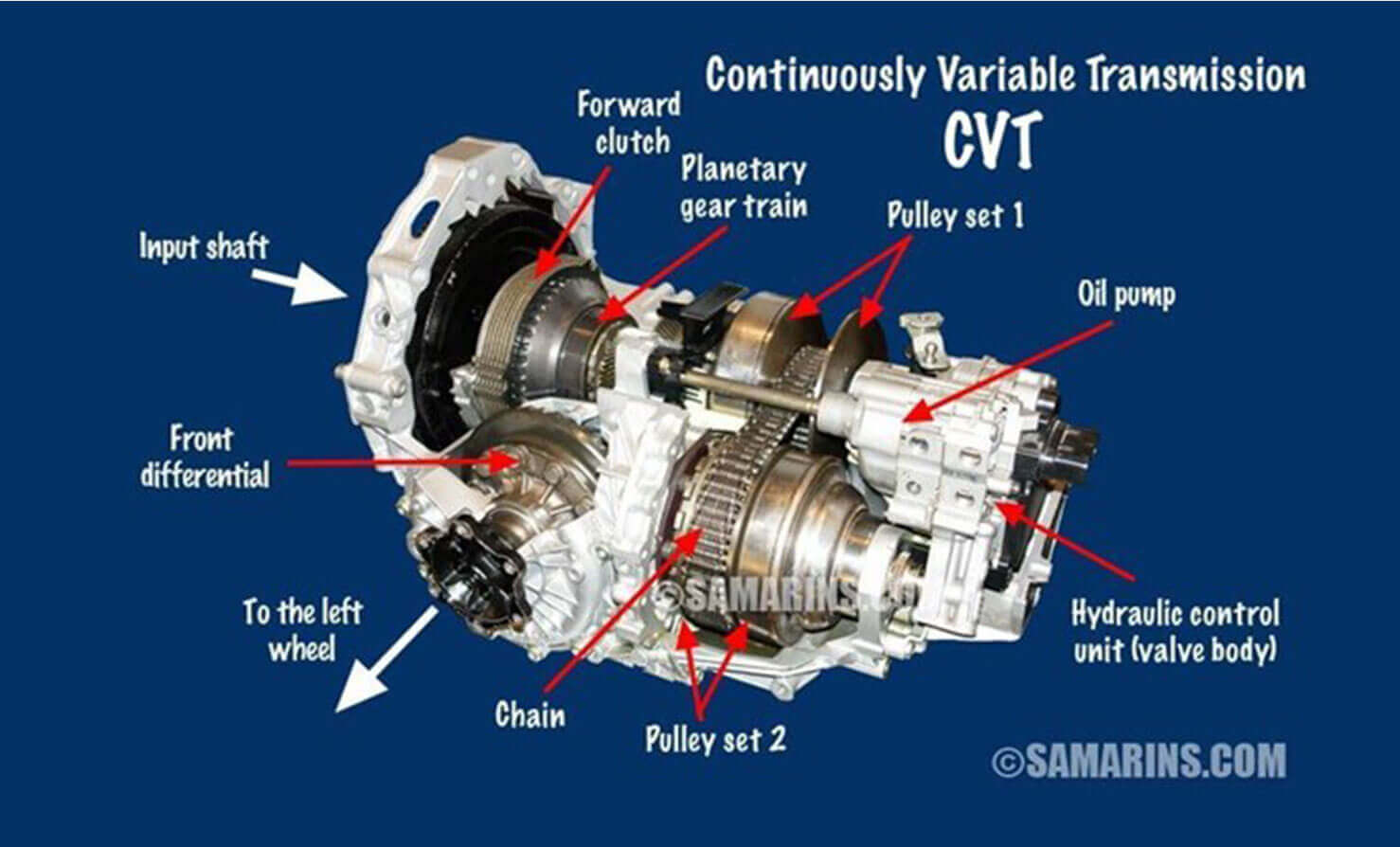
At its core, the CVT employs a simple yet sophisticated mechanism involving belts and pulleys that adjust their diameter as the vehicle moves. This adjustment allows the transmission to change the engine’s output speed without interruptions from changing gears.
Advantages Over Other Transmissions:
- Efficiency: Operates the engine at the most efficient RPM for a range of vehicle speeds.
- Smoothness: Delivers a smoother drive with no noticeable gear changes.
Types of CVT
Continuously Variable Transmissions (CVTs) come in several types, each designed for specific applications and performance needs.
Here’s a brief overview of the main types of CVTs and their typical uses:
Pulley-Based CVT
- Overview: This is the most common type of CVT, found primarily in small to medium-sized cars.
- Mechanism: It uses a system of variable-diameter pulleys connected by a belt or chain, allowing for seamless changes in gear ratios.
- Applications: Widely used in passenger vehicles by manufacturers like Toyota, Honda, and Nissan. It’s favored for its fuel efficiency and smooth driving experience.
Toroidal CVT
- Overview: Toroidal CVTs use discs and rollers instead of pulleys and belts.
- Mechanism: The system involves input and output discs with rollers that tilt to change the contact points, providing variable gear ratios.
- Applications: Suitable for performance vehicles due to its higher torque capacity. It is used in some luxury and high-performance models to offer both power and smooth acceleration.
Hydrostatic CVT
- Overview: This type of CVT uses hydraulic fluid to transfer power.
- Mechanism: It employs a hydraulic pump and motor to convert mechanical energy to hydraulic pressure and back, allowing for continuous variation in gear ratios.
- Applications: Ideal for heavy-duty applications like agricultural and industrial machinery. Its robustness and precise control make it suitable for equipment that requires reliable power and durability.
Each type of CVT has specific benefits and is tailored to meet the demands of different driving and operational environments. Pulley-based CVTs are known for their efficiency and smoothness, toroidal CVTs for their high torque capacity, and hydrostatic CVTs for their durability and precise control in heavy machinery.
Discover More: Types of CVT
Advantages of CVT
CVTs offer several benefits that make them an attractive choice for a variety of vehicles and applications:
Fuel Efficiency
- Optimal Engine Speed: CVTs maintain the engine at its most efficient RPM, reducing fuel consumption compared to traditional automatic transmissions.
- Real-World Data: Studies have shown that CVT-equipped vehicles often achieve better fuel economy, particularly in city driving and stop-and-go traffic.
Durability
- Fewer Moving Parts: CVTs have fewer moving parts than conventional transmissions, which reduces wear and tear.
- No Gear Shifts: The absence of gear shifts means less stress on transmission components, contributing to a longer lifespan and potentially lower maintenance costs.
Control
- Precise Power and Speed Control: CVTs provide more precise control over power delivery and speed combinations, resulting in smoother acceleration and a more responsive driving experience.
- Enhanced Driving Experience: The continuous adjustment of the gear ratio ensures a seamless transition between speeds, offering a more comfortable and enjoyable drive.
These advantages are supported by real-world data and case studies from various industries, demonstrating the role of CVTs in enhancing vehicle performance and efficiency. By offering improved fuel efficiency, durability, and control, CVTs are increasingly favored by both manufacturers and drivers.
Learn More: CVT Transmission Pros and Cons
Common Problems with CVT
While CVTs offer numerous benefits, they are not without their issues. Here are some common problems associated with CVTs:
Reliability Concerns
- Durability Issues: Some CVT models may experience durability problems, especially under high-stress conditions or heavy loads. This can lead to premature wear and tear of the transmission components.
- Component Failure: The belt or chain in a pulley-based CVT, for example, can wear out or fail, leading to costly repairs.
Maintenance Costs
- Higher Costs: Maintenance and repair costs for CVTs can be higher than for traditional transmissions due to the specialized parts and technology involved.
- Frequent Fluid Changes: CVTs require regular fluid changes with specific types of transmission fluid, which can add to the maintenance expenses.
Identifying and addressing these problems early can prevent more serious issues and extend the life of the transmission. Regular maintenance and prompt attention to any signs of trouble are essential for ensuring the longevity and reliability of a CVT.
Read More: CVT Transmission Problems
Understanding Transmission Sounds
Recognizing unusual noises in a CVT (Continuously Variable Transmission) can help diagnose issues early and potentially prevent costly repairs.
Here are some common transmission sounds and what they might indicate:
High-Pitched Whining
- Cause: A high-pitched whining noise from a CVT often indicates issues with the transmission fluid. It could be low fluid levels, old or degraded fluid, or the wrong type of fluid.
- Action: Check the transmission fluid level and condition. If the fluid is low, add the appropriate type recommended by the manufacturer. If the fluid looks dirty or burnt, consider getting it changed. If the noise persists, have the transmission inspected by a professional.
Clunking or Banging
- Cause: Clunking or banging noises can be caused by several issues, including worn or damaged internal components such as bearings, pulleys, or the belt. It could also be a sign of a more serious mechanical problem within the transmission.
- Action: This type of noise usually requires immediate attention from a professional mechanic. Driving with a clunking transmission can cause further damage and potentially lead to a complete transmission failure.
Humming or Buzzing
- Cause: Humming or buzzing noises can indicate issues with the transmission fluid pump or the solenoids. These components are responsible for regulating the flow of transmission fluid and controlling the transmission’s operation.
- Action: If you hear a humming or buzzing noise, have your vehicle inspected to check the fluid pump and solenoids. These parts may need to be repaired or replaced.
Grinding
- Cause: Grinding noises are often a sign of severe wear or damage to the internal components of the transmission, such as gears, bearings, or the CVT belt.
- Action: Grinding noises should not be ignored. Immediate professional inspection is required, and driving should be minimized to prevent further damage.
Rattling
- Cause: Rattling noises can occur due to loose or damaged parts within the transmission or the surrounding components. This could be something as simple as a loose heat shield or a more serious issue within the CVT.
- Action: Investigate any rattling noise promptly. While some causes might be minor and easy to fix, others could indicate a significant problem that needs professional attention.
Detailed Guide: Transmission Noises: What They Mean: Transmission Noises: What They Mean
CVT Maintenance and Care
Regular maintenance is crucial for the longevity and optimal performance of a CVT (Continuously Variable Transmission). By following a consistent maintenance routine, you can prevent major issues, enhance the efficiency of your vehicle, and extend the lifespan of your transmission. Here are the key aspects of CVT maintenance and care:
- Routine Checks: Regular inspections and fluid changes.
- Professional vs. DIY: Understanding when professional help is required.
Adhering to a maintenance schedule can significantly extend the life of your CVT and ensure its performance remains consistent.
More on Maintenance: CVT Transmission Repair
FAQs about CVT
What is the efficiency of CVT compared to manual transmissions?
CVT transmissions are generally more efficient than traditional automatic transmissions but can vary in efficiency when compared to manual transmissions. CVTs can continuously adjust the engine’s RPM to operate at the most efficient point, often resulting in better fuel economy under certain driving conditions. However, manual transmissions can still be more efficient in specific scenarios, especially when driven by an experienced driver who can optimize gear changes for fuel savings. Overall, CVTs tend to offer better fuel efficiency in city driving and stop-and-go traffic, whereas manuals may excel in highway driving.
What maintenance does a CVT require?
Maintaining a CVT transmission is crucial for its longevity and performance. Key maintenance tasks include:
- Regular Fluid Changes: CVT transmissions require specific types of fluid that need to be checked and replaced according to the manufacturer’s schedule. Using the correct fluid is vital, as the wrong type can cause significant damage.
- Periodic Inspections: Regular inspections by a professional mechanic can help identify potential issues early. This includes checking for leaks, unusual noises, or signs of wear.
- Software Updates: Some CVTs rely on software for optimal performance, so keeping the transmission control software up-to-date is important.
- Avoid Overloading: Avoid excessive towing or carrying heavy loads, as this can put additional strain on the CVT.
- Driving Habits: Smooth and steady driving without abrupt acceleration or deceleration can help extend the life of a CVT.
What are common signs that there might be a problem with my CVT transmission?
Common signs of CVT transmission issues include unusual noises such as whining or grinding, a burning smell, slipping or jerking during acceleration, hesitation or surging at certain speeds, and the illumination of the check engine light. If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to have your vehicle inspected by a professional as soon as possible.
Call to Action
Interested in learning more about how CVT can benefit your vehicle? Contact our experts today for in-depth advice and support.
A Name You Can Trust
© 2026 Copyright. Advanced Transmission Center. All rights reserved.